Marketing success doesn’t happen by accident. Behind every winning campaign lies a strategic framework that guides decision-making and drives results. The 3Cs of marketing—Company, Customers, and Competitors—form the foundation of this strategic approach.
This framework helps businesses understand their position in the market while identifying opportunities for growth. By analyzing these three critical elements, you can create marketing strategies that resonate with your audience and outperform the competition.
Understanding the 3Cs Marketing Framework
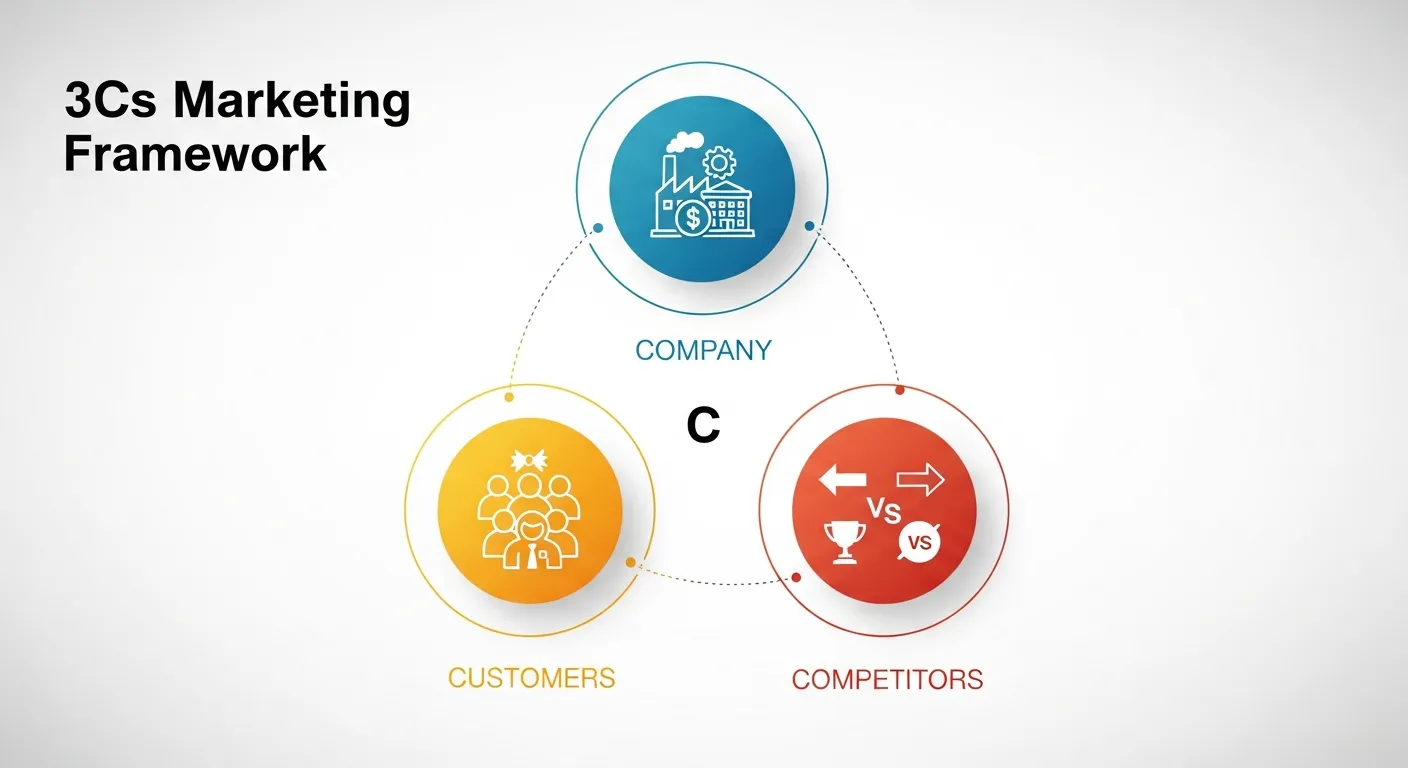
The 3Cs model was developed by business strategist Kenichi Ohmae in the 1980s. This framework provides a structured approach to analyze three fundamental aspects of any business environment.
Each component plays a vital role in shaping your marketing strategy:
- Company: Your internal strengths, resources, and capabilities
- Customers: Your target audience’s needs, preferences, and behaviors
- Competitors: The competitive landscape and market dynamics
When used together, these elements create a comprehensive view of your business environment. This analysis helps you make informed decisions about positioning, messaging, and resource allocation.
The First C: Company Analysis
Your company analysis examines internal factors that influence marketing success. This deep dive into your organization reveals what makes you unique and how to leverage those strengths.
Assessing Your Core Strengths
Start by identifying what your company does exceptionally well. These strengths become the foundation of your marketing message and competitive advantage.
Consider these key areas:
Resources and Capabilities: What unique assets does your company possess? This might include proprietary technology, skilled personnel, or established partnerships.
Brand Reputation: How do customers perceive your brand? Strong brand equity can differentiate you from competitors and justify premium pricing.
Operational Excellence: Where does your company excel in delivery, quality, or customer service? These operational strengths often translate into powerful marketing messages.
Identifying Internal Challenges
Honest self-assessment includes recognizing areas for improvement. Understanding your weaknesses helps you address them proactively or position them strategically.
Common internal challenges include limited resources, skill gaps, or outdated systems. Acknowledging these limitations helps you set realistic marketing goals and allocate resources effectively.
Defining Your Value Proposition
Your company analysis should culminate in a clear value proposition. This statement articulates why customers should choose you over alternatives.
An effective value proposition addresses three questions:
- What specific benefits do you provide?
- Who receives these benefits?
- How are you different from competitors?
The Second C: Customer Analysis

Understanding your customers goes beyond basic demographics. Deep customer analysis reveals motivations, behaviors, and unmet needs that drive purchasing decisions.
Segmenting Your Market
Not all customers are created equal. Market segmentation helps you identify distinct groups within your broader market, each with unique characteristics and needs.
Effective segmentation considers multiple factors:
Demographic Segmentation: Age, income, education, and other statistical characteristics provide a foundation for understanding your market.
Psychographic Segmentation: Values, attitudes, and lifestyle preferences offer deeper insights into customer motivation.
Behavioral Segmentation: Purchase history, brand loyalty, and usage patterns reveal how customers interact with your category.
Geographic Segmentation: Location-based factors can influence preferences and purchasing power.
Understanding Customer Needs
Successful marketing addresses real customer needs. This requires moving beyond what you think customers want to understand what they actually need.
Primary research methods like surveys, interviews, and focus groups provide direct customer insights. Secondary research through industry reports and market studies offers a broader context.
Pay attention to both expressed needs (what customers say they want) and latent needs (underlying desires they might not articulate). Innovation often comes from addressing unmet latent needs.
Mapping the Customer Journey
Modern customers interact with brands across multiple touchpoints. Understanding this journey helps you optimize each interaction for maximum impact.
Map out the typical customer journey from awareness to purchase and beyond. Identify key touchpoints where customers form opinions about your brand. This mapping reveals opportunities to improve the customer experience and remove friction from the buying process.
The Third C: Competitor Analysis
Competitor analysis provides crucial context for your marketing strategy. Understanding the competitive landscape helps you identify opportunities and avoid costly mistakes.
Identifying Your Competition
Start by defining your competitive set. This includes direct competitors offering similar products and indirect competitors addressing the same customer needs differently.
Consider multiple levels of competition:
Direct Competitors: Companies offering similar products to the same target market
Indirect Competitors: Alternative solutions that address the same customer problem
Substitute Products: Different approaches to meeting customer needs
Analyzing Competitive Positioning
Study how competitors position themselves in the market. This analysis reveals gaps you can exploit and positioning strategies to avoid.
Examine competitor messaging, pricing strategies, and target audiences. Look for patterns in how they communicate value propositions and differentiate themselves.
Learning from Competitive Strengths and Weaknesses
Competitive analysis isn’t about copying what others do. Instead, it’s about understanding what works and identifying opportunities for differentiation.
Study successful competitor campaigns to understand effective tactics and messaging. Equally important, learn from competitor mistakes to avoid similar pitfalls.
The Role of Data and Analytics in the 3Cs Framework
Data and analytics play a pivotal role in refining your marketing strategy based on the 3Cs framework. By leveraging data, you can make more informed decisions in each of the three categories: Company, Customers, and Competitors.
How Data Enhances Company Analysis
Company analysis requires understanding your internal resources and capabilities, but data can refine this process. Metrics like customer satisfaction scores, employee performance, and operational efficiency provide concrete evidence of your company’s strengths and weaknesses. Using business intelligence tools, you can analyze trends over time, compare internal performance, and identify areas for improvement that might not be immediately obvious.
Customer Data: Deepening Insights
Customer analysis is all about understanding needs, behaviors, and preferences. Data analytics, including customer surveys, CRM systems, and website analytics, help you gain deeper insights into customer segments, purchasing behaviors, and pain points. By tracking customer interactions across multiple touchpoints, you can also create more personalized marketing messages and customer journeys that increase engagement and loyalty.
Competitor Data: Staying Ahead of the Curve
Competitor analysis doesn’t just rely on manual research; data can provide you with critical insights into your competition’s performance. Using tools like social media analytics, SEO tracking, and industry reports, you can monitor your competitors’ strategies, identify gaps in their offerings, and pinpoint emerging threats. This data-driven approach ensures that your competitor analysis is as accurate and up-to-date as possible.
Integrating the 3Cs for Strategic Advantage
The real power of the 3Cs framework emerges when you analyze all three elements together. This integrated approach reveals strategic opportunities that single-element analysis might miss.
Finding Your Sweet Spot
Look for the intersection where your company’s strengths meet customer needs in ways that competitors haven’t addressed. This sweet spot represents your best opportunity for competitive advantage.
This analysis might reveal:
- Underserved customer segments
- Unique value propositions
- Competitive gaps to exploit
- New market opportunities
Developing Positioning Strategy
Use your 3Cs analysis to develop a positioning strategy that sets you apart. Effective positioning communicates your unique value in terms that resonate with target customers.
Your positioning should be:
- Relevant: Addresses important customer needs
- Differentiated: Clearly distinct from competitors
- Credible: Supported by your company’s capabilities
- Sustainable: Difficult for competitors to replicate
Creating Tactical Marketing Plans
With strategic positioning established, you can develop Traditional Marketing Tactics plans that support your overall strategy. These tactics should leverage your strengths while addressing customer needs in competitively advantageous ways.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid

Many companies struggle with 3Cs analysis due to common mistakes. Avoiding these pitfalls improves the quality of your analysis and resulting strategy.
Overemphasizing Internal Perspectives
Companies often focus too heavily on their own capabilities while neglecting customer and competitive perspectives. This internal focus can lead to marketing messages that don’t resonate with target audiences.
Balance internal analysis with external market research. What matters most is how customers perceive your capabilities, not just what you think you do well.
Underestimating Competitive Threats
Competitive landscapes change rapidly. Yesterday’s minor competitor might become tomorrow’s market leader. Regular competitive monitoring helps you stay ahead of emerging threats.
Don’t limit your analysis to obvious competitors. Disruption often comes from unexpected sources that approach your market differently.
Static Analysis
The 3Cs framework requires ongoing attention. Market conditions, customer preferences, and competitive dynamics evolve continuously.
Establish regular review cycles to update your analysis. This ongoing process ensures your strategy remains relevant and effective.
The 3Cs in Action: Real-World Examples of Strategic Success
The 3Cs framework is more than just a theoretical model; it’s been used by numerous successful companies to inform their marketing strategies. Below, we’ll explore how a few notable brands have implemented the 3Cs approach to drive success.
Company Example: Apple’s Brand Strategy
Apple’s marketing strategy is a textbook example of how the 3Cs framework can work in practice. Apple’s internal strengths lie in its brand reputation, innovation, and user-friendly design. This is reflected in the company’s marketing messages that highlight simplicity and elegance. Their customer analysis focuses on creating a seamless user experience across all touchpoints, ensuring customer loyalty. In terms of competitors, Apple strategically positions itself as a premium brand, differentiating itself from other tech giants like Samsung by offering a unique combination of design, ecosystem, and customer service.
Customer Example: Starbucks’ Personalization
Starbucks uses customer analysis and segmentation to create personalized experiences that keep customers coming back. Through its loyalty program, mobile app, and data-driven marketing campaigns, Starbucks analyzes customer purchasing behavior to send personalized offers and recommendations. This level of customer-centric marketing is designed to make each customer feel valued. Starbucks’ marketing also emphasizes community engagement, which aligns with its customer-centric approach and builds a stronger emotional connection with its audience.
Competitor Example: Coca-Cola vs. Pepsi
Coca-Cola and Pepsi have been locked in competition for decades, making them prime examples of how to leverage competitor analysis. Coca-Cola focuses on the emotional connection with customers, emphasizing happiness, family, and celebration. Pepsi, on the other hand, often targets a younger, more rebellious demographic with its edgy, music-driven campaigns. Both brands have used the 3Cs to position themselves as leaders in the soft drink industry, with Coca-Cola focusing on tradition and Pepsi appealing to a sense of youthfulness and excitement. Their competitive strategies continue to evolve in response to each other’s moves, showcasing the dynamic nature of the 3Cs framework.
Bringing It All Together: Your Marketing Success Strategy

The 3Cs of marketing provide a proven framework for developing strategies that work. By systematically analyzing your company, customers, and competitors, you create a foundation for marketing success.
Remember that effective implementation requires commitment and consistency. Use your 3Cs analysis to guide decision-making across all marketing activities, from campaign development to resource allocation.
Start by conducting a thorough 3Cs analysis of your current situation. Identify the key insights that emerge from this analysis and use them to refine your marketing strategy. With this foundation in place, you’ll be equipped to create marketing campaigns that truly connect with your audience and drive business results.